PCM vs DPCM vs ADPCM-Difference between PCM,DPCM,ADPCM modulations
This page on PCM vs DPCM vs ADPCM describes difference between PCM, DPCM and ADPCM modulation techniques.All these are pulse digital modulation techniques.
PCM
Cool Music Converter is a wizard-styled audio converter utility program that allows you to convert audio files between WAV, OGG Vorbis, MP3, MP2, Microsoft ADPCM, WMA, VOX, AAC, M4A, AMR and other well-known media formats according to your wish. It seamlessly integrates into Windows and is always accessible without having to bring up a clunky, screen-hogging interface. Cool Music Converter is a wizard-styled audio converter utility program that allows you to convert audio files between WAV, OGG Vorbis, MP3, MP2, Microsoft ADPCM, WMA, VOX, AAC, M4A, AMR and other well-known media formats according to your wish.It seamlessly integrates into Windows and is always accessible without having to bring up a clunky, screen-hogging interface. ADPCM can achieve compression ratios of up to 4:1. The implementation of ADPCM for XAudio2 provides additional features to specify the size of the compression sample block. ADPCM enables the audio designer to choose a setting that is an appropriate compromise among size, quality, and resolution (for placing loop points).
The short form of the Pulse Code Modulation is PCM. In PCM, the analog speech waveform is sampled and converted directly intoa multibit digital code by an Analog to Digital converter.The digital code is stored in the memory and which is later re-called for theplayback.
In this type of modulation, analog data is sampled and quantized before being represented to digital binaryform. Hence using PCM, continuous amplitude and continuous time signal waveform is converted into discrete amplitude and discrete timewaveform.
If there is a n bit quantizer and sampling rate is Fs then bit rate will be
Rb(bits/sec) = n * Fs
Sampling rate must be at a rate greater than or equal to nyquist rate to avoid aliasing.Higher the sampling rate easier is the reconstruction at the receiver.Bandwidth requirement is minimum Rb/2 and maximum Rb.
Signal to Quantization Noise Ratio for PCM for sinusoidal input is
SQNR (dB) = 6*n + 1.76, where n is bit of uniform quantizer.
DPCM
The short form of Delta Pulse Code Modulation is DPCM.In DPCM, a multi-bit difference value is stored.A bipolar D/A converter is used for playback to convert the successive difference valuesto an analog waveform.
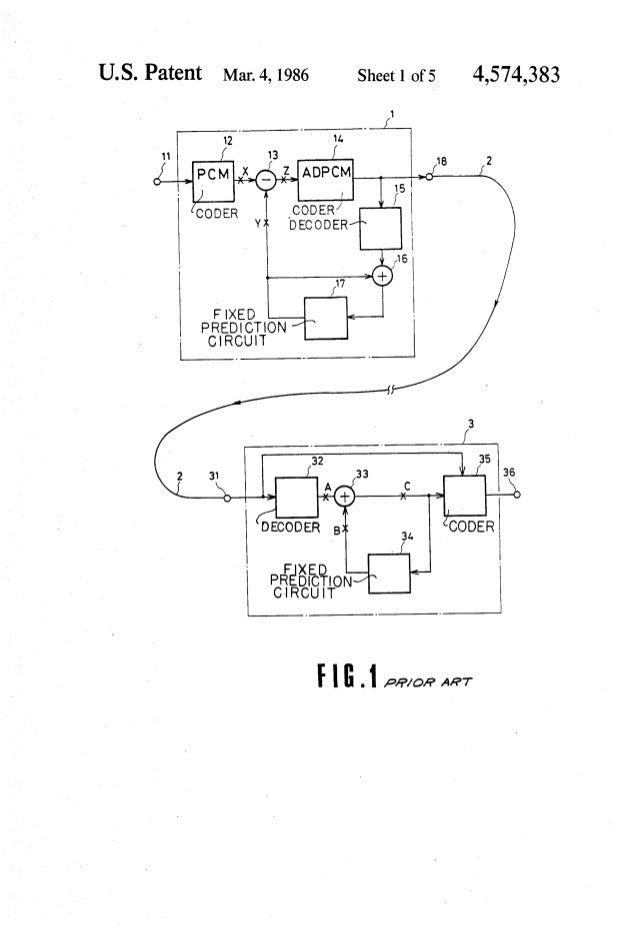
Figures 1 and 2 depicts DPCM encoder and DPCM decoder block diagram.
This modulation scheme encodes difference in current as well as predicted values.
Simple block diagram of linear predictor used in DPCM is depicted in the fig3.
When the samples of a signal are highly correlated then we go for DPCM in order to save bandwidth or usingthe same bandwidth at higher data rate.
Delta Modulation
It is a special case of differential PCM.It is called 1 bit DPCM as it transmits only one bit per sample.
In delta modulation problem of slope overload occurs if input is changing very fast that is :
| Δ/Ts | < | dm(t)/dt |
Adpcmwaveformat
To overcome slope overload error we choose optimum size of Δ such that :
Δopt/Ts = | dm(t)/dt |max
For m(t) = Am*cos(2*π*fm*t)
Δopt/Ts = 2*π*fm*Am
The second problem occurs is hunting, which occurs when message is almost constant.
ADPCM
In adaptive delta modulation, step size is chosen in accordance with message signal sampled value to overcomeslope overload error and hunting.
If message is varying at a high rate then step size is high and if message is varying slowly then step size is small.
The short form of Adaptive Delta Pulse Code Modulation is ADPCM.In ADPCM, a difference value that has been mathematically adjusted accordingto the slope of the input waveform is stored. Bipolar D/A converter is used to convert the stored digital codeto analog for playback.
Figures 4 and 5 depicts ADPCM encoder and ADPCM decoder block diagram.
Refer advantages and disadvantages ofPCM >>,DPCM >> andADPCM >> techniques.
Modulation types
BPSK -This page describes BPSK modulation technique with equation and constellation diagram.
QPSK -This page describes QPSK modulation technique with equation and constellation diagram.
QAM-This page describes QAM modulation technique with equation and constellation diagram.
MSK-GMSK MSK modulation,GMSK modulation and GMSK demodulation.
8PSK 8-PSK modulation or multilevel PSK or phase shift keying modulation technique.
BPSK vs QPSK -Difference Between BPSK and QPSK modulation techniques.
QPSK vs OQPSK vs pi/4QPSK-Difference between QPSK,OQPSK and pi/4QPSK modulation techniques
Differential Encoder and Decoder
What is Difference between
FIR filter Vs. IIR filter
difference between FDM and OFDM
Difference between SC-FDMA and OFDM
Difference between SISO and MIMO
Difference between TDD and FDD
Difference between 802.11 standards viz.11-a,11-b,11-g and 11-n
OFDM vs OFDMA
CDMA vs GSM
Bluetooth vs zigbee
Convert Ulaw To Wav Free
RF and Wireless Terminologies
Share this page
Translate this page
Adaptive differential pulse-code modulation (ADPCM) is a variant of differential pulse-code modulation (DPCM) that varies the size of the quantization step, to allow further reduction of the required data bandwidth for a given signal-to-noise ratio.
Typically, the adaptation to signal statistics in ADPCM consists simply of an adaptive scale factor before quantizing the difference in the DPCM encoder.[1]
ADPCM was developed for speech coding by P. Cummiskey, Nikil S. Jayant and James L. Flanagan at Bell Labs in 1973.[2]
In telephony[edit]
In telephony, a standard audio signal for a single phone call is encoded as 8000 analog samples per second, of 8 bits each, giving a 64 kbit/s digital signal known as DS0. The default signal compression encoding on a DS0 is either μ-law (mu-law) PCM (North America and Japan) or A-law PCM (Europe and most of the rest of the world). These are logarithmic compression systems where a 13 or 14 bit linear PCM sample number is mapped into an 8 bit value. This system is described by international standard G.711. Where circuit costs are high and loss of voice quality is acceptable, it sometimes makes sense to compress the voice signal even further. An ADPCM algorithm is used to map a series of 8 bit μ-law (or a-law) PCM samples into a series of 4 bit ADPCM samples. In this way, the capacity of the line is doubled. The technique is detailed in the G.726 standard.
Some ADPCM techniques are used in voice over IP communications. ADPCM was also used by Interactive Multimedia Association for development of legacy audio codec known as ADPCM DVI, IMA ADPCM or DVI4, in the early 1990s.[3]

Split-band or subband ADPCM[edit]
G.722[4] is an ITU-T standard wideband speech codec operating at 48, 56 and 64 kbit/s, based on subband coding with two channels and ADPCM coding of each.[5] Before the digitization process, it catches the analog signal and divides it in frequency bands with QMF filters (quadrature mirror filters) to get two subbands of the signal. When the ADPCM bitstream of each subband is obtained, the results are multiplexed and the next step is storage or transmission of the data. The decoder has to perform the reverse process, that is, demultiplex and decode each subband of the bitstream and recombine them.
Referring to the coding process, in some applications as voice coding, the subband that includes the voice is coded with more bits than the others. It is a way to reduce the file size.
Software[edit]
The Windows Sound System supported ADPCM in WAV files.[6]
Wav To Adpcm Converter Online
The FFmpeg audio codecs supporting ADPCM are adpcm_ima_qt, adpcm_ima_wav, adpcm_ms, adpcm_swf and adpcm_yamaha.[7][8]
See also[edit]
- Pulse-code modulation (PCM)
References[edit]
Xbox Adpcm Converter
- ^Ken C. Pohlmann (2005). Principles of Digital Audio. McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN978-0-07-144156-8.
- ^Cummiskey, P.; Jayant, Nikil S.; Flanagan, James L. (September 1973). 'Adaptive quantization in differential PCM coding of speech'. The Bell System Technical Journal. 52 (7): 1105–1118. doi:10.1002/j.1538-7305.1973.tb02007.x.
- ^Recommended Practices for Enhancing Digital Audio Compatibility in Multimedia Systems - legacy IMA ADPCM specification, Retrieved on 2009-07-06
- ^ITU-T G.722 page ITU-T Recommendation G.722 (11/88), '7 kHz audio-coding within 64 kbit/s'
- ^Jerry D. Gibson; Toby Berger; Tom Lookabaugh (1998). Digital Compression for Multimedia. Morgan Kaufmann. ISBN978-1-55860-369-1.
- ^'Differences Between PCM/ADPCM Wave Files Explained'. KB 89879 Revision 3.0. Microsoft Knowledge Base. 2011-09-24. Archived from the original on 2013-12-31. Retrieved 2013-12-30.
- ^'FFmpeg General Documentation - Audio Codecs'. FFmpeg.org. Retrieved 2013-12-30.
- ^'FFmpeg/adpcmenc.c at ee4aa388b2231e988eccdab652c55df080d6ad45 · FFmpeg/FFmpeg'. GitHub. 2017-02-15. Retrieved 2018-02-05.