- Wwtp Design Software Free Windows 10 Pc
- Wwtp Design software, free downloads
- Wwtp Design Software Free Windows 10
- Wwtp Design software, free download
- Wwtp Design Software Free Online
Software
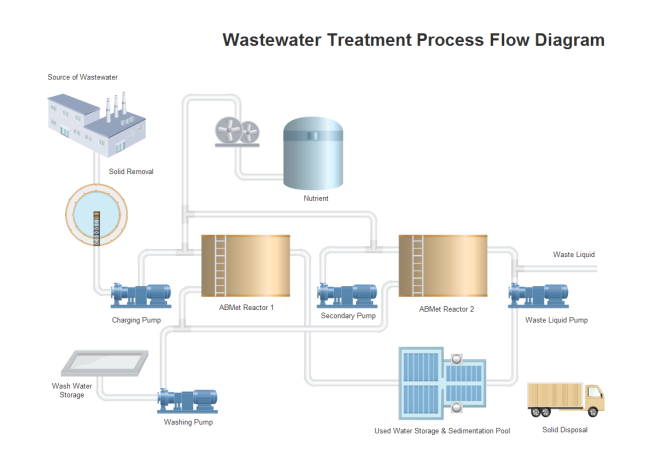
Reasons to use Transcend Design Generator: You can't bid on as many projects as you want to. Your clients want results faster, with more detail, at lower cost. You spend too much time on the first 20-30% of the design. You want to offer clients more design alternatives and options. Treatment, Optimization and Design for WWTP's - Environmental - Environmental Management. The purpose of the work is to demonstrate the rationale, procedures and advantages of using process simulation to evaluate the steps involved in process upgrades from conventional or fully aerobic process conditions to multi stage systems capable of operating as a BNR system.
- A software for the integrated design of wastewater treatment plants.
- BioWin is used worldwide to design, upgrade, and optimize wastewater treatment plants of all types. The core of BioWin is our proprietary biological model which is supplemented with other process models (e.g. Water chemistry models for calculation of pH and precipitation reactions, mass transfer models for oxygen modeling and other gas-liquid.
ASIM
ASIM (Activated Sludge SIMulation Program) is a simulation program, which allows for the simulation of a variety of different biological wastewater treatment systems:
Activated sludge systems with up to 10 different reactors in series (aerobic, anoxic, anaerobic), including sludge return and internal recirculation streams, batch reactors, chemostat reactors, etc.
More information on ASIM
The program allows for the definition of process control loops (simple proportional controllers and on/off type binary controllers) and dynamic simulation of load variation (diurnal or seasonal load variation, temperature variation, variation of operational parameters such as aeration, excess sludge removal, recycle rates etc.).
Data analysis is supported by the possibility to compare observed data with simulation results in easy to use graphic support routines. Simulated results may be exported to spreadsheets for further treatment.
A menu driven user interface with context sensitive help information (by pressing F1 key), graphic support and simple file handling makes the program easy to use in class rooms, research and commercial applications.
The special feature of ASIM is that biokinetic models (the different materials or components used to characterize the wastewater and the transformation processes with relevant stoichiometry and kinetics) may be freely defined, stored and edited by the user. This allows the researcher to develop his own specific model and it allows the student to learn modelling by stepwise increase of model complexity. Simple as well as complex models are distributed together with the program in the model library. The distribution file includes copies of the Activated Sludge Model No.1 (adapted), No.2d as well as ASM3 as proposed by the IAWQ Task Group for Mathematical Modelling for Design and Operation of Biological Wastewater Treatment.
The teaching and research version of ASIM 5 is now available free of charge.
The commercial version of ASIM 5 is available for CHF 2000.
Contact
Publication
Organic matter, light and contaminant degradation

'Let's talk cash': Cantons' interests and the reform of Swiss federalism
Description of the program ASIM
Dynamic Simulation Software for Biological Wastewater Treatment Modeling
ASIM 5 is a key design tool indispensable for
- engineering and consulting companies
- sewage treatment plant operators
- contractors
- environmental authorities
- Research and Development (R & D)
- applications engineering
and anyone who is engaged in construction, refurbishment, operation and optimation of biological sewage treatment plants.
Features
- analysis of the actual state
- dynamic modeling
- determination of load limits
- simulation of specific operating conditions
- examination of spare capacity
- elaboration of control concepts
- plant optimation
Biological Sewage Treatment - Marked by New Dynamics
Complex biotechnological processes are applied in current municipal domestic wastewater treatment. Dynamic simulation of critical process conditions can help to prevent operational failure or to determine load limits and spare capacity. Thus an optimal performance of these complex processes even under difficult circumstances can be ensured.
The common way of dimensioning biological wastewater treatment systems is to use static models and calculations. Rules of thumb along with calculations are applied to describe operational conditions that can be compared to real situations. However, these static models cannot cope with time variation. The effects of time-related phenomena can be described by dynamic simulation only.

ASIM 5 allows for the dynamic simulation of diurnal load variation, peak loads, specific operating conditions, etc. The effects of such variations on any process parameter of the plant can be investigated. The simulation is based on the biokinetic model.

Diurnal load variation / related concentration plots for several system parameters
Both simple and complex models are issued in a model database that comes along with the program. The distributed version includes copies of the Activated Sludge Model No.1, No. 2, and No. 3, as proposed by the IAWQ Task Group for Mathematical Modeling for Design and Operation of Biological Wastewater Treatment. In addition, the model database contains versions of the IAWQ Models No. 2 and No. 3 that have been modified by EAWAG/ETH. The special feature of ASIM is that biokinetic models may be freely defined, stored and edited by the user.
The program has been developed under the supervision of Prof. Willi Gujer at the Institute for Hydromechanics and Water Resources Management, ETH Zurich. The latest scientific insights and simulation models have been integrated in the current version ASIM 5.
System requirements ASIM 5 English
Operating system: Windows® 95 or higher ; screen resolution: 800 x 600 VGA (opt. 1024 x 768); RAM > 32 MB; available hard-disk space approx. 5 MB
Parametrizing levels for process parameter input and data evaluation

Functional range of ASIM 5
- dynamic simulation of load variation, process alteration and adjustment of operational parameters such as aeration, excess sludge removal, recycle rates, etc.
- definition of control loops
- data analysis facilitated by easy to use graphic support routines for comparison of observed data with simulation results
- analysis and simulation of activated sludge systems with up to 10 different reactors in series, including biological phosphorus removal, return sludge, internal recirculation, batch reactors, chemostatic reactors, sequencing batch reactors, etc.
- user-friendly interface on Windows® operating systems with numerous export functions
- further treatment systems such as alternating/intermittent treatment and further biokinetic models such as anaerobic sludge digestion are currently being implemented
TEMPEST
TEMPEST is a simulation program, which allows for the simulation of dynamics of the wastewater temperature in sewers in connection to heating with wastewater.
More information on TEMPEST
TEMPEST is an interactive simulation program for temperature estimation in sewers. It can be used to calculate the dynamics and longitudinal spatial profiles of the wastewater temperature in sewers. Applications range from simple steady state estimations of the changes of the wastewater temperature in a single sewer line to full scale simulations of the dynamics of the wastewater temperature in successive sewer lines with lateral inflows.
Program Availability
Wwtp Design Software Free Windows 10 Pc
The current program version of TEMPEST is 'Version 1.02'. In order to receive the TEMPEST executable file, please fill out the download form.
Wwtp Design software, free downloads
Screenshots
References
A mathematical model to predict the effect of heat recovery on the wastewater temperature in sewers
Simulation of the wastewater temperature in sewers with TEMPEST
Wwtp Design Software Free Windows 10
Wwtp Design software, free download
Contact
Wwtp Design Software Free Online
For general enquiries please send an e-mail to tempest@cluttereawag.ch.
Documentation
- TEMPEST User Manual and Software License (for Version 1.02)[2.30MB]
- Example Model Files (case study manual)[245KB]
- TEMPEST Excersice PEAK Course A28/08 (in German)[100KB]
- Model files for PEAK Course Exercise[231KB]